ZEBRIS FDM-T treadmill
The treadmill is a system for the quantitative, biomechanical assessment of gait and body posture. It is equipped with a transmission belt with a matrix of measuring sensors transmitting the signal to the computer in real time. Dedicated software for the FDM-T treadmill enables to analyze the distribution of pressure forces on the ground while walking and standing. It allows the analysis of the individual phases of gait and the evaluation of many parameters describing the gait, including speed, stride length and width, foot positioning while walking and stride symmetry. The static software module allows to analyze the pressure of the feet on the ground while standing freely. The change in the position of the center of pressure on the ground (CoP) over time is also determined. It allows to determine the sway of the body and assess the balance. The treadmill can be synchronized with a high-resolution video camera and EMG. It can also be part of a larger measurement system.
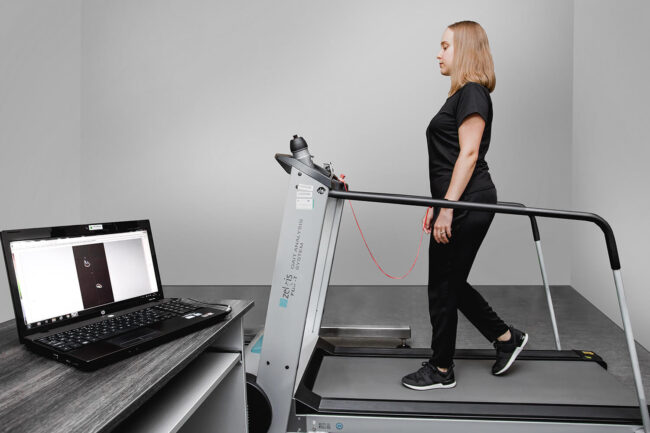

Examples of ZEBRIS FDM-T treadmill applications:
- assessment of gait abnormalities in children and adults, assessment of gait symmetry (screening tests),
- evaluation of the effectiveness of the applied locomotive functions enhancement,
- evaluation of running, running style, balance during dynamic activities,
- assessment of the balance of neurological and geriatric patients,
- assessment of changes in the foot pressure distribution on the ground while using various types of orthopedic equipment.
Biodex SYSTEM 4 PRO
The BIODEX isokinetic assessment and training system enables isokinetic and isometric assessment of the musculoskeletal system based on active or passive movement in the trunk and joints including the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee and ankle. It is equipped with dynamometers that allow to measure the moments of muscle strength in the joints in dynamic conditions during concentric and eccentric work with the possibility of changing the speed of the movement.
The chair allows to measure the moments of muscle strength during isometric exercises as well as isokinetic exercises that are carried out at a constant speed. It also allows to measure proprioception. It is used during rehabilitation as well as conducting and monitoring sports training. The system is equipped with a mobile workstation with a control panel.
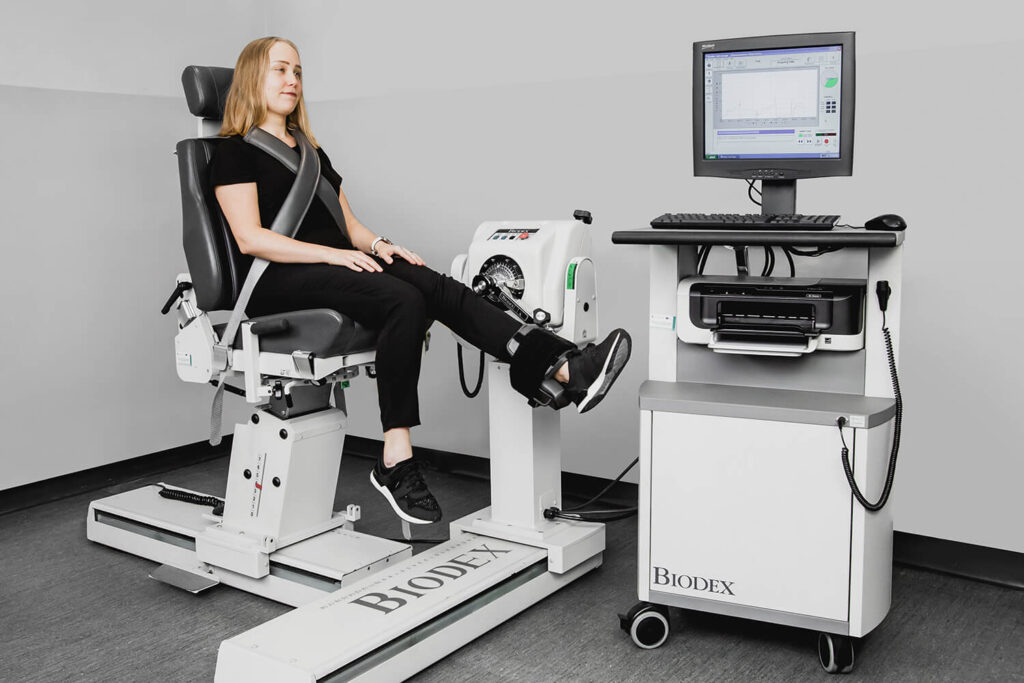

Examples of research possibilities:
- isokinetic and isometric evaluation of the motor system based on active or passive movement of the torso or in the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee or ankle joints,
- measurement muscle strength moments during isometric exercises as well as isokinetic exercises that are conducted at a constant speed,
- measurement of proprioception.
ZEBRIS APGMS Pointer
It’s a non-invasive diagnostic and measuring system for recording and dynamic analysis of body movement and posture. The system is based on the ultrasound technology measuring distances between sensors placed on the patient’s body.
The examination consists in showing characteristic anatomical points on the patient’s skeleton with the ultrasound indicator. These points are treated by the software as passive points (as opposed to active points, which are two markers of the point indicator). Their position and possible movement (static or dynamic test) are tracked and recorded in real time in the software.


The ZEBRIS APGMS system can be used e.g. for:
- objective assessment of posture and figure in a static position,
- assessment of the range of motion and shape of curves during specific tests (e.g. Schober or Otto),
- analysis of spine movement patterns in all planes,
- assessment of the range of mobility of individual sections of the spine and the total mobility of the pelvis and spine for the ergonomics and sport purposes,
- assessment of the symmetry of individual anthropometric points,
- assessment of the relative alignment (tilt) of body segments.
Noraxon compression dynamometer
The Noraxon compression dynamometer is one of the many biomechanical sensors for the Noraxon wireless system. This device allows to measure the grip force of the hand using built-in isometric sensor based on a strain gauge. Additionally, it has a special area for measuring the strength of the thumb.
Tests with the use of a dynamometer allow for the following:
- assessment of the grip strength of the examined person,
- measurement of reaction time for any sound or visual stimulus,
- measurements in psychomotor tests of both children and professional drivers

Noraxon TeleMyo2400 G2
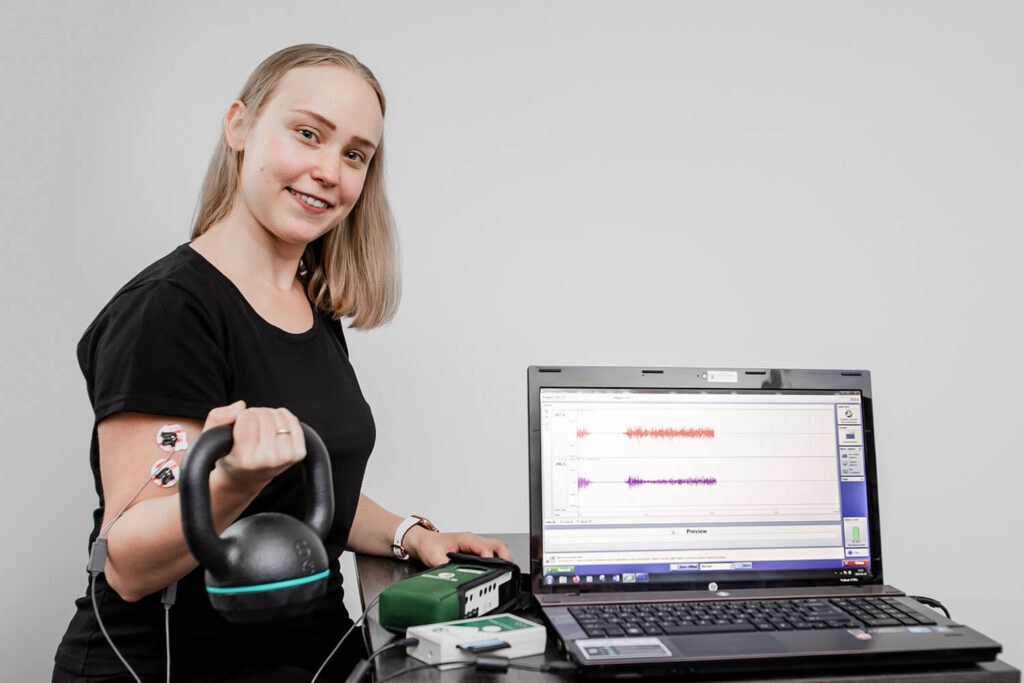

Noraxon TeleMyo2400 G2 is a wireless EMG measurement system. It allows to measure the surface EMG signal. Thanks to the USB transmitter and receiver, the measurement data is sent in real time to a PC or laptop up to a distance of 100 m. The system allows the measurement of up to 32 active EMG leads. Thanks to the compatibility with many biomechanical sensors (by replacing the EMG cable with a particular sensor on any analog port), i.e. a compression dynamometer, accelerometer, goniometer or biomonitor, it is possible to record reliable, time-synchronized data, which allows for comprehensive tests for physicians, researchers or physiotherapists.
EMG examination allows to:
- determine the type of muscle disorder,
- help in the selection of appropriate therapeutic procedures to reduce the existing disorders.
Zebris FDM-S platform
It is a multifunctional platform for measuring the force density distribution. The Zebris FDM-S platform consists of individually calibrated capacitive force sensors enabling the analysis of the density distribution of static and dynamic forces arising under the feet while standing and walking. It enables computer diagnostics of feet and loads in static (standing, sitting, etc.) and dynamic conditions. Measurements can be made by examining the effects of wearing shoes on gait or posture. The dynamic module of the software enables the analysis of the distribution of the foot pressure forces on the ground during the passage through the platform.
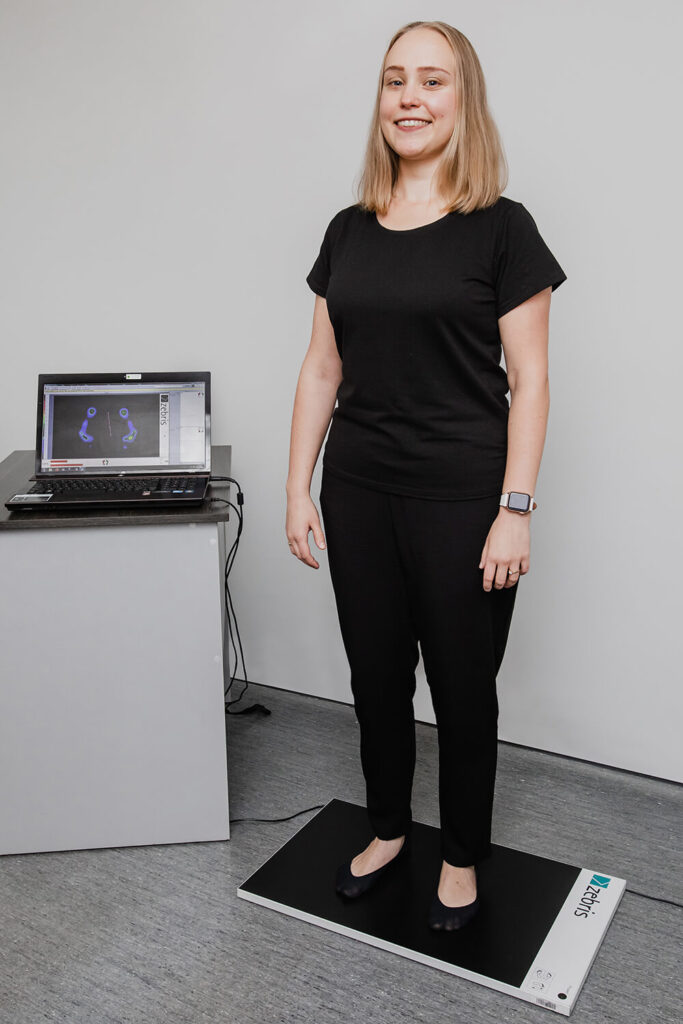
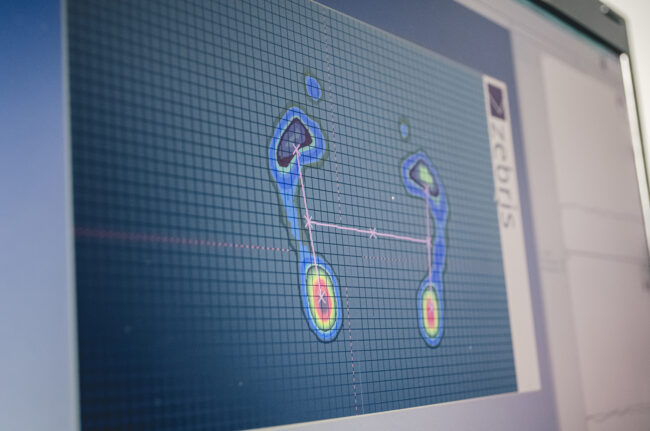


Examples of the Zebris FDM-S platform applications:
- assessment of the ability to maintain balance based on stabilographic tests,
- assessment of the symmetry of loading the feet while standing freely,
- assessment of load distribution on individual foot segments,
- assessment of the ground reaction forces while walking,
- assessment of the ground reaction forces during various exercises, e.g. squats, sitting down and getting up from a chair, etc.
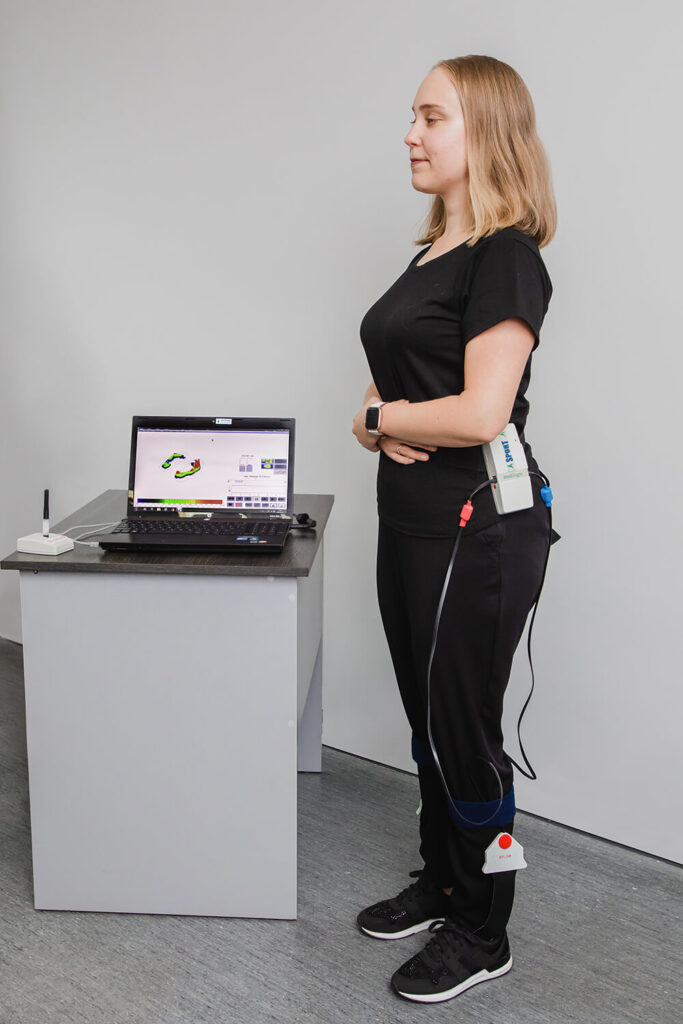
Inertial XSENS motion analysis system
Inertial system for analyzing the movement XSENS is a system consisting of wireless IMU sensors placed on the body with straps / tapes. Each of the sensors includes a three-axis accelerometer, gyroscope, and magnetometer. The system allows for wireless measurement of kinematic data of any movement with high accuracy in all three planes, in real time. Special software enables the acquisition, visualization and processing of data from wireless sensors. The system allows, among others, for measuring: position, velocity and acceleration of individual body segments in space, assessment of the position of the torso, pelvis, head and angles in the joints, assessment of the position of the center of body mass. The system is equipped with a video camera, so it is possible to synchronize the obtained results with the film.
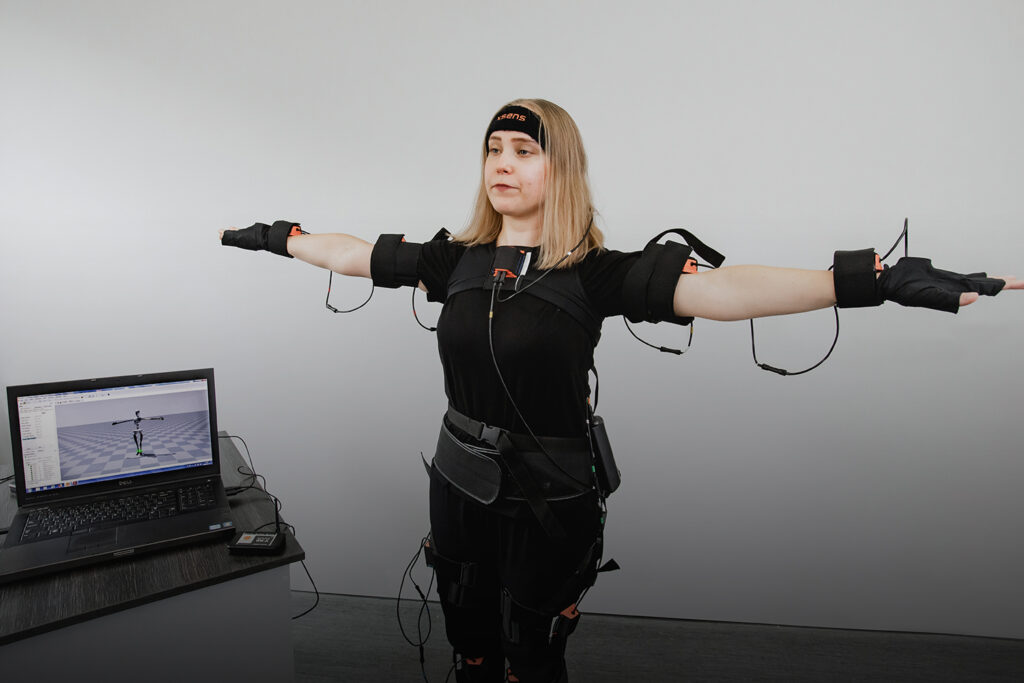
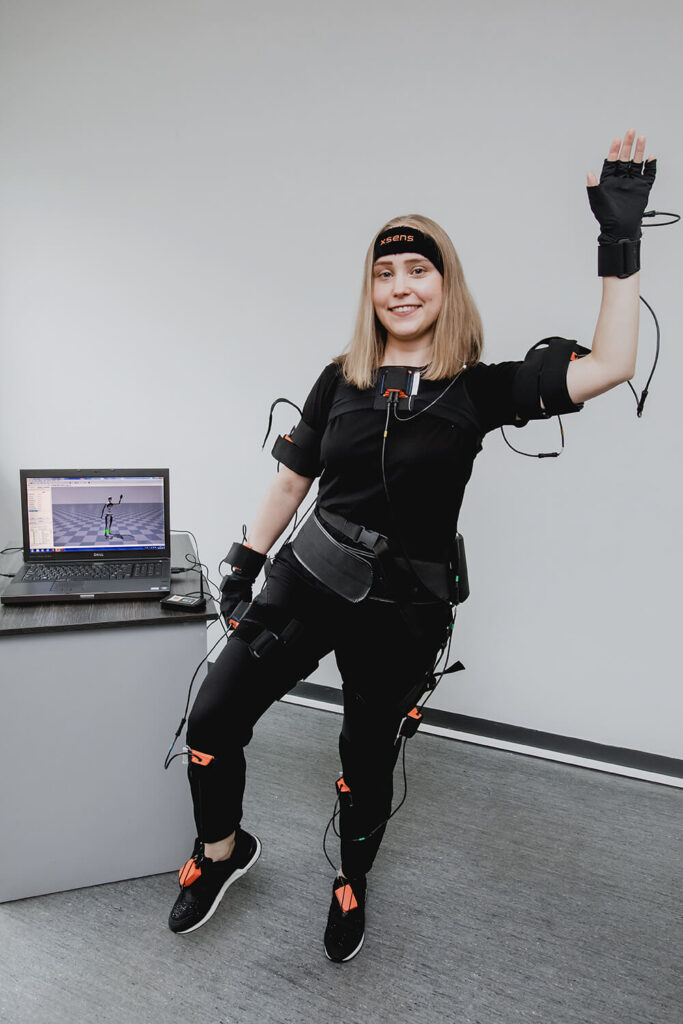




Examples of applications of the inertial system for motion analysis:
- evaluation of the effectiveness of rehabilitation,
- quantitative assessment of movement,
- registration of movements for computer animations used in rehabilitation,
- athletes’ movement assessment,
- optimization of sports training,
- detection of falls,
- assessment of the ergonomics of movement in the workplace, e.g. at workstations exposed to monotypic work movements,
- creating computer animations for computer games, films, medicine, etc.
Medilogic Insoles
MEDILOGIC INSOLES are insoles for the assessment of load distribution – in other words, it is a system for recording and assessing load distribution using inserts placed directly in the shoes of the examined person.
The system of footwear inserts allows to measure the distribution of forces on the sole of the foot. The system is based on the technology of baro-resistive sensors with the possibility of viewing data in real time and enables wireless data transfer from the inserts via modem to the computer. The system includes a set of measuring inserts for footwear that allow to determine the distribution of pressure on the foot and the vertical reaction of the ground during the implementation of various forms of movement: walking, running, climbing and descending stairs or other physical activities (including sports).
The advantage of the system is the ability to make continuous measurements for 30s to 360s, with a sampling frequency of 60Hz-240Hz.

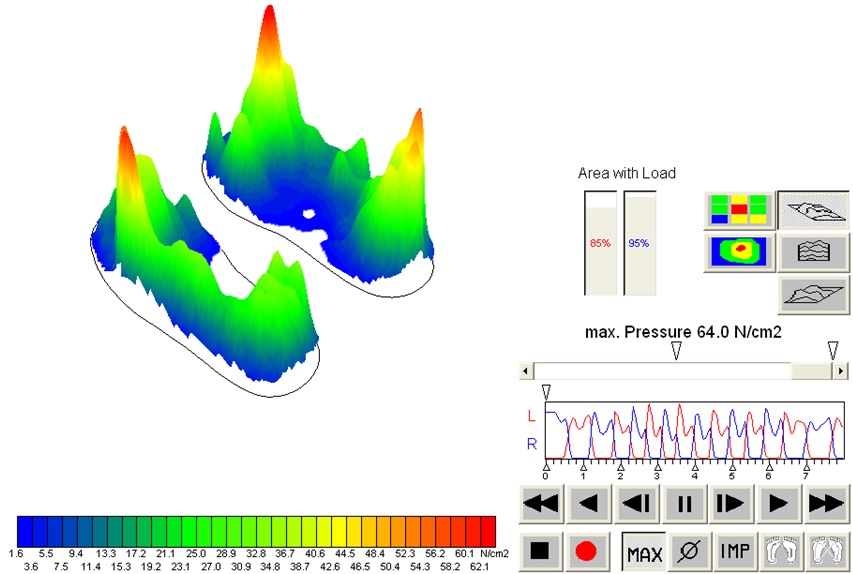
Examples of inserts applications:
- assessment of gait abnormalities and asymmetry,
- supporting to compensation eliminating training,
- assessment of forces during contact with the ground, especially when running (increased loads),
- identification of zones of increased foot load,
- assessment of the performance of the musculoskeletal system, assessment of the running style and body balance during dynamic activities,
- analysis of plantar pressure distribution in various forms of physical activity,
- assessment of changes in load distribution depending on the type of prosthetic and orthopedic equipment used.
AMTI platforms
A set of two AMTI platforms enables the measurement of various forms of human locomotion. Each of the platforms allows for the measurement of three components of the ground reaction force. The signal from the measurement sensors is sent to a computer workstation.
Software allows for collecting measurement data and their analysis, as well as for training with biofeedback.
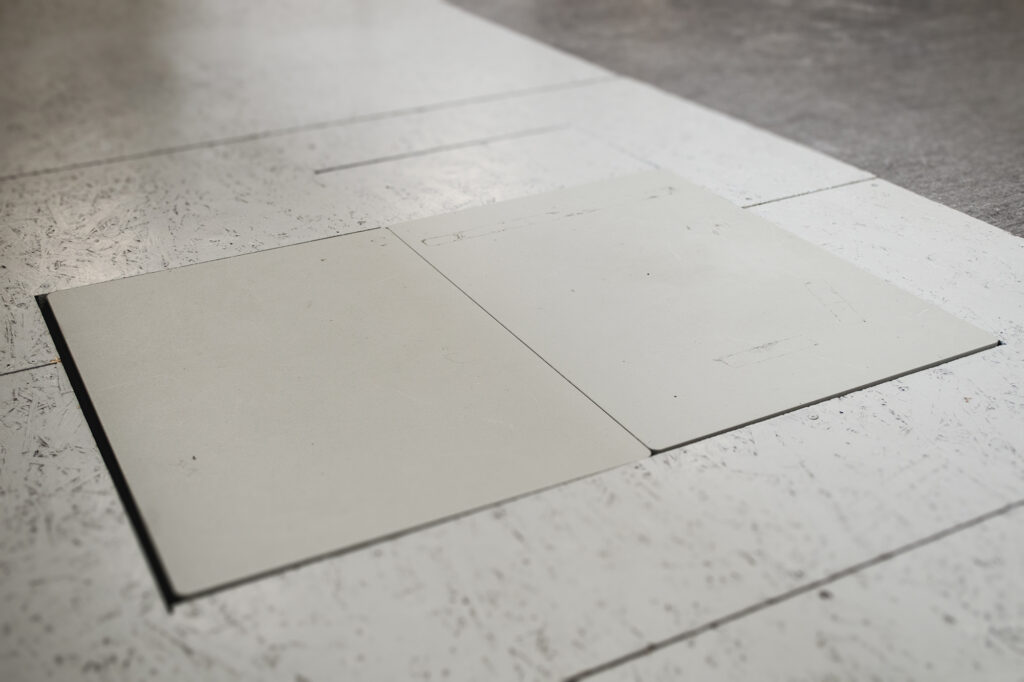


Examples of AMTI platforms applications:
- assessment of strength and speed abilities based on the work and power generated by the lower limbs during vertical jump,
- measurement of ground reaction forces during locomotion (walking, running),
- stabilographic tests based assessment of the ability to maintain balance.
